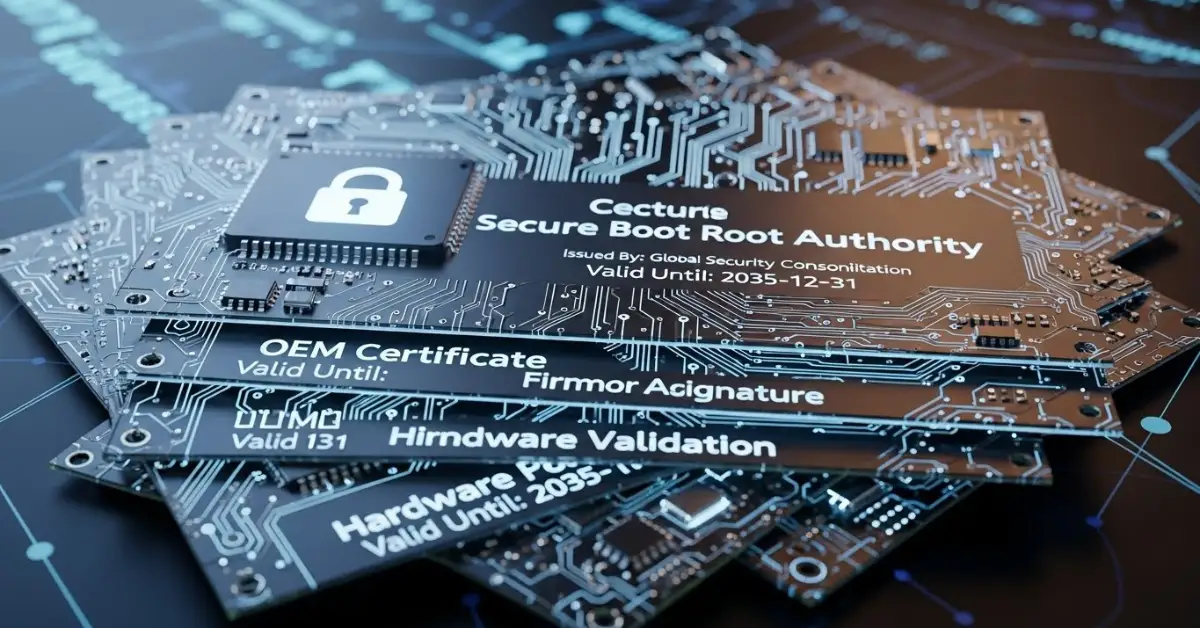
In mid-2026, an important change is coming to Windows security: several Secure Boot certificates used by anti-cheat systems are reaching their expiration dates. Secure Boot is a core security feature designed to ensure your PC only runs trusted software at startup. When its certificates expire, anti-cheat software that depends on them may fail to operate until updated certificates are installed.
In mid-2025, an important change is coming to Windows security: several Secure Boot certificates used by anti-cheat systems are reaching their expiration dates. Secure Boot is a core security feature designed to ensure your PC only runs trusted software at startup. When its certificates expire, anti-cheat software that depends on them may fail to operate until updated certificates are installed.
What Is Secure Boot and Why It Matters
1. Secure Boot Explained
Secure Boot is a UEFI firmware feature that verifies the authenticity of software before it runs during system startup. This process uses cryptographic certificates to confirm that only approved, trusted software, including operating systems and driver,s loads when you turn on your PC.
By preventing unsigned or tampered code from executing, Secure Boot helps protect against malware that targets the boot process, such as rootkits and bootkits.
2. How Secure Boot Works
Secure Boot relies on certificates stored in firmware. During startup, the PC checks each component’s digital signature against these certificates. If the signature is valid, the component loads; if not, loading is blocked. This creates a hardware-level trust chain that enhances system security from the ground up.
Why Certificates Are Expiring in 2026
➡️Certificate Lifecycles and Renewal
Digital certificates, including those used by Secure Boot, are not permanent; they have expiration dates as a security measure. Expiration helps ensure that cryptographic keys are periodically refreshed, reducing the risk of compromise.
In June 2026, several certificates embedded in the Secure Boot database, including those relied upon by major anti-cheat systems, are scheduled to expire. Without updated certificates, affected software may no longer pass Secure Boot verification.
➡️Anti-Cheat Dependencies on Secure Boot
Some anti-cheat systems integrate deeply with Secure Boot to enforce security guarantees at the kernel level. These systems use specific certificates to validate their components during boot and at runtime. When a certificate expires, the anti-cheat software may not initialize correctly or could be blocked by Secure Boot entirely.
What This Means for Gamers
1. Potential Launch Issues
Games that depend on affected anti-cheat systems could fail to launch or display errors related to anti-cheat integrity checks. This situation can be frustrating for players who may see abrupt launch failures without clear messaging.
2. In-Game Disruptions
Even if games launch, online play may be restricted or disabled if anti-cheat cannot validate properly under Secure Boot. Competitive multiplayer titles could be most impacted, as anti-cheat enforcement is a standard requirement for these experiences.
3. Temporary Workarounds
In the short term, developers may suggest:
- Updating games and anti-cheat software to the latest versions
- Installing new certificates via Windows Update or partner installers
- Ensuring Secure Boot remains enabled in UEFI settings
However, temporary fixes could vary by vendor, and staying informed about updates is essential.
Responses from Software Vendors and Platform Providers
➡️Certificates in Transit
Manufacturers of anti-cheat software and PC platform providers have reportedly prepared updated Secure Boot certificates to replace those expiring in June 2026. These replacements are being distributed through official update channels, such as:
- Windows Update
- Anti-cheat partner updates
- Firmware (UEFI) updates from OEMs
The goal is to ensure that by the time the old certificates expire, new ones are already installed or ready to install.
➡️Coordinated Deployment Strategy
Because delayed certificates could disrupt multiple anti-cheat systems simultaneously, vendors are coordinating updates well in advance. This reduces the risk that players will encounter broken launches or online restrictions when certificates expire.
How to Prepare Your PC for the Transition
1. Keep Windows Updated
Ensuring your system has the latest Windows updates is one of the most reliable ways to receive updated certificates. Microsoft routinely delivers firmware and security updates through its standard update channels.
2. Update Anti-Cheat Services
Most anti-cheat providers have integrated update mechanisms within game launchers or as standalone services. Allow these to update automatically so that any new certificate dependencies are resolved without manual intervention.
3. Verify Secure Boot Status
Check your system’s UEFI settings to confirm that Secure Boot is enabled and functioning. Navigate to your motherboard’s firmware settings to verify Secure Boot status and certificate enrollment if necessary.
Addressing Common Concerns
➡️Will Expiry Break My System?
A Secure Boot certificate expiration does not inherently “break” Windows. Instead, it affects how specific security software, particularly kernel-level anti-cheat system,s verifies its components. Most users will be unaffected if they keep their system and software up to date.
➡️Can I Disable Secure Boot to Bypass Issues?
Disabling Secure Boot may temporarily allow affected software to run, but it also lowers system security. It exposes the machine to boot-level threats and is generally not recommended unless directed by official support steps.
➡️Are Third-Party Tools Impacted?
Only software that integrates with Secure Boot certificates for integrity validation will be affected. Most applications that operate in user space (outside of kernel or boot processes) will continue to function normally.
How Certificate Updates Are Delivered
1. Windows Update
Microsoft often includes updated secure boot certificates as part of cumulative updates delivered through Windows Update. Keeping automatic updates enabled helps ensure you receive these changes promptly.
2. Anti-Cheat Software Updates
Some anti-cheat partners may deliver certificates or signing updates via their own launchers or update platforms. Make sure these are set to automatically update to prevent potential launch issues.
3. OEM Firmware Updates
System manufacturers (Dell, HP, Lenovo, etc.) may include Secure Boot certificate updates in firmware (UEFI) updates. Check your PC or motherboard manufacturer’s support page for updates beyond what Windows Update provides.
Real-World Scenarios to Expect
Gamers With Automatic Updates
If your system receives timely updates and you run supported anti-cheat tools, the certificate transition should be seamless. Most modern Windows setups with automatic updates enabled will install necessary certificates before expiration.
Users With Manual Update Settings
Users who delay updates or disable automatic installations may encounter issues after June 2025. Manually checking for updates and installing firmware as released helps prevent problems.
Competitive Multiplayer Players
Players who focus on competitive titles, especially those that enforce strict anti-cheat policies, should be extra vigilant about updates. Being early to install updated anti-cheat versions ensures uninterrupted online play.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion
The upcoming expiration of key Secure Boot certificates in mid-2026 highlights the importance of regular updates and proactive system maintenance. While this event could disrupt certain anti-cheat software if ignored, coordinated efforts from software vendors and platform providers mean that updated certificates are already being distributed through official channels.
For gamers and everyday users alike, the best defense against compatibility issues is to keep your system, drivers, and security services current. With timely updates and proper configuration, your PC will remain secure and capable of running all supported software without interruption.
Staying informed and prepared ensures a smooth transition through this certificate lifecycle event one that reinforces Windows’ commitment to trusted computing and long-term security.